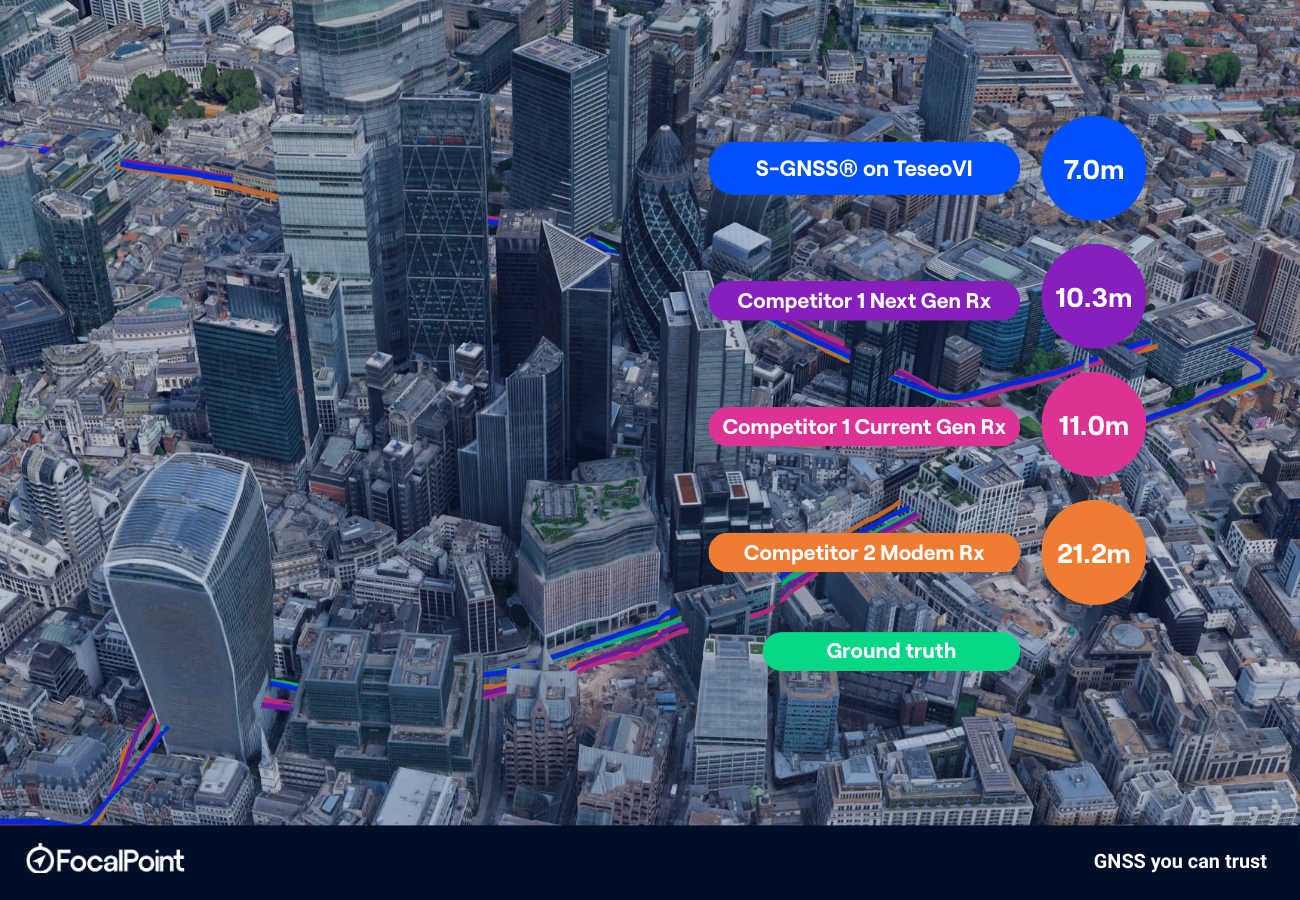
In this blog post, Jez Ellis-Gray, Product Lead at FocalPoint, presents the results of our competitive analysis comparing S-GNSS on Teseo with standard industry solutions. The cover image represents horizontal position accuracy at 95%, reflecting the numbers in Table 1.
Introduction
FocalPoint’s S-GNSS® Auto: Reliable GNSS in urban environments
S-GNSS® Auto is Focal Point Positioning’s software technology built on Supercorrelation® – an advanced GNSS processing approach that boosts direct line-of-sight signals while attenuating multipath and reflected interference. In urban environments, where traditional receivers can be misled by reflections from buildings and vehicles, S-GNSS improves measurement quality at the source. The result is enhanced reliability, improved positioning consistency, and greater resilience in challenging signal conditions.
STMicroelectronics and FocalPoint: S-GNSS on Teseo devices
S-GNSS is integrated into STMicroelectronics’ Teseo GNSS receivers, a leading platform in the automotive market. Teseo devices are deployed in millions of vehicles worldwide and are widely recognised for their performance and reliability. Our integration combines ST’s automotive-grade GNSS hardware with Focal Point’s Supercorrelation processing, creating a joint solution aimed at delivering best-in-class urban positioning performance without requiring changes to vehicle architecture. S-GNSS operates directly at the measurement level, improving the quality of pseudorange and related signal inputs by prioritising line-of-sight signals and mitigating multipath effects. While this enhancement occurs “under the hood”, its impact is clear and visible in the position domain, as demonstrated in the results below.
Our Evaluation Kits (EVKs) enable automotive partners to test and validate our solution in their own environments using the Teseo platform. S-GNSS® Auto is available on TeseoV and TeseoVI for OEMs, Tier 1s and navigation engine providers.
The Benchmarking Trial
To evaluate performance, we conducted a recent drive trial in central London — a representative dense urban environment with narrow streets, high-rise buildings, open squares, and varying traffic conditions. During the trial, we benchmarked the Teseo + S-GNSS solution against three commercial competitor GNSS receivers under the same conditions. The goal was to compare real-world positioning performance across key metrics and determine the measurable benefit delivered by S-GNSS when integrated into an automotive-grade receiver.
Method
Car Setup
To ensure an objective and repeatable comparison, the trial vehicle was instrumented with a high-accuracy ground truth system alongside a controlled GNSS replay architecture.
A NovAtel survey-grade antenna paired with a PwrPak7 GNSS/IMU system was mounted on the vehicle roof to generate centimetre-level ground truth positioning. This reference system provided tightly coupled GNSS and inertial measurements, enabling highly reliable position, velocity and altitude estimates throughout the route, including in challenging urban sections.
In parallel, raw RF GNSS data was captured during the drive. This RF log file formed the basis of our benchmarking approach. The recorded RF data was then replayed 5 times using a LabSat 3W system into all test receivers. Each of the 5 sets of data was then aggregated to provide the results shown below.
This replay-based setup ensures fairness, repeatability, and direct comparability — eliminating environmental variability and allowing performance differences to be attributed solely to receiver and signal-processing behaviour rather than changing sky conditions.
Route
The drive route is shown below in green. The route takes in the toughest multipath London has to offer, providing the receivers with a difficult but real-world challenge.
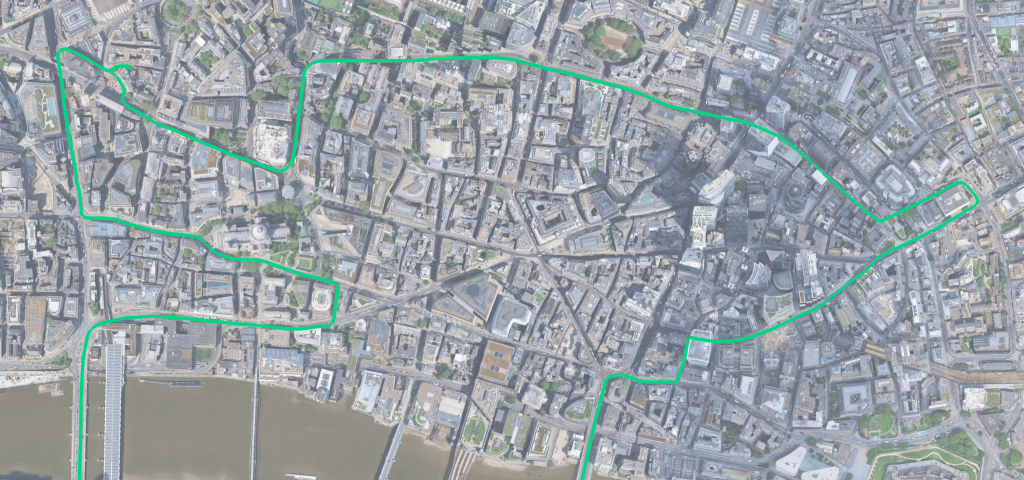
Fig 1: The drive route around London as provided by the NovAtel ground truth system. Please note this section is part of a longer drive, but all data shown below is the ‘deep-urban’ section of the drive, north of the River Thames.
Analysis & Results
In this blog we present the analysis of the horizontal position error, as well as some sample route segments showing the visual performance differences on a map view. Results presented in this study are position-domain and generated using the test receiver outputs and the Ground Truth system. In each of the receivers, the internal Navigation Engines are used to produce the results. More detailed analysis, including measurement domain and additional route segments, is available on request.
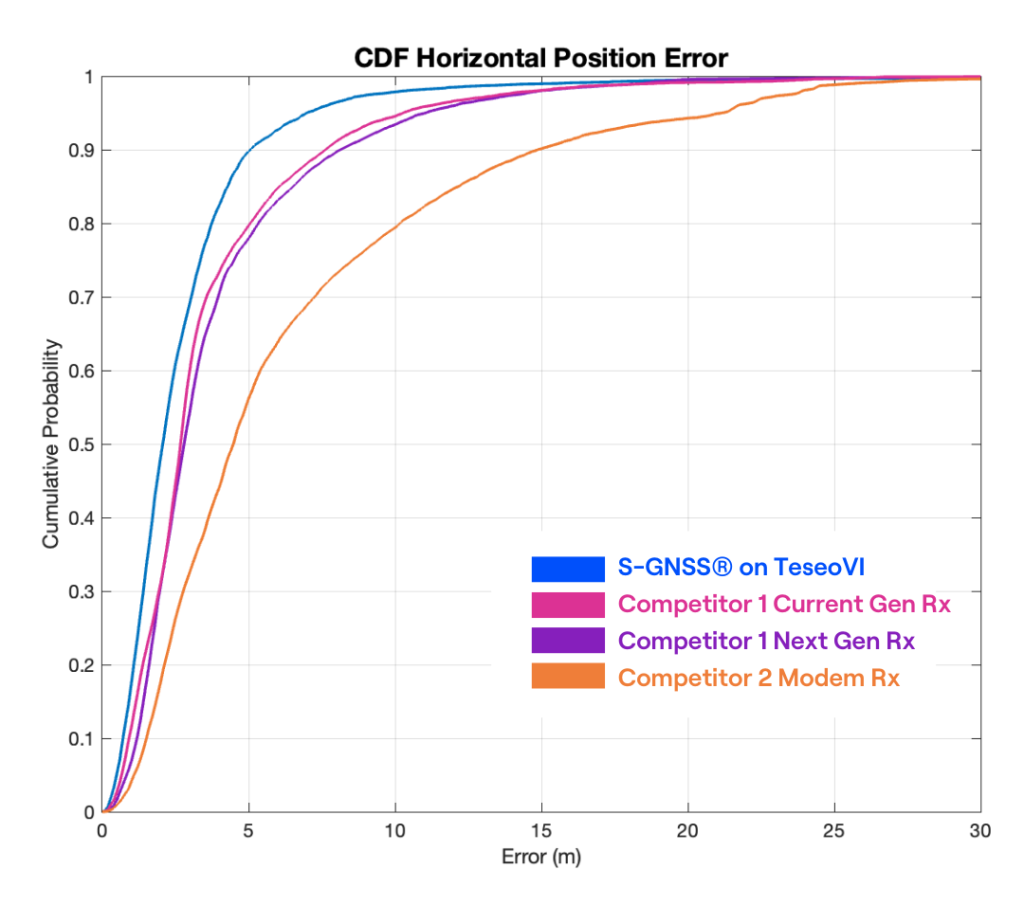
Figure 2: A Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) chart of the Horizontal (2D) Position Error of ST Teseo+S-GNSS (blue) and 3 competitor devices (pink, purple and orange).
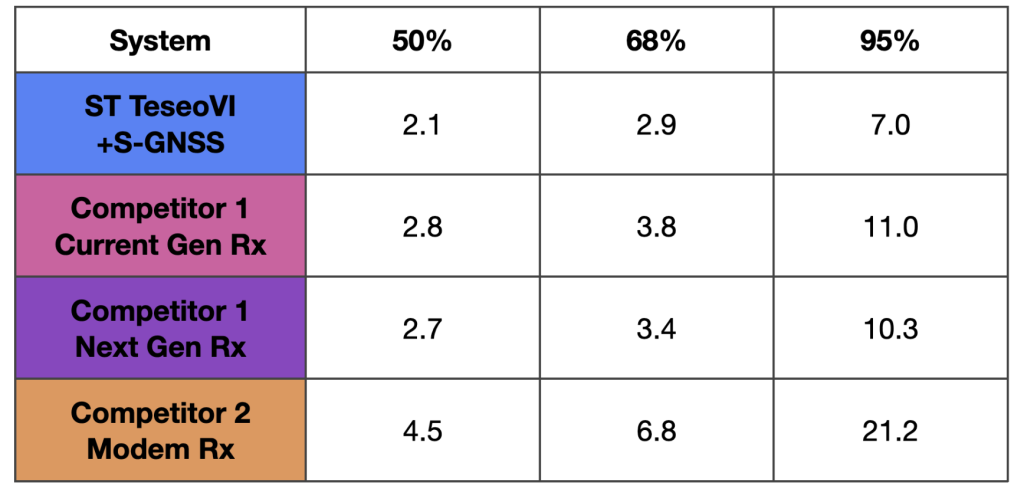
Table 1: The horizontal position errors, in metres, at 50, 68 and 95% associated with the CDF in Figure 2.
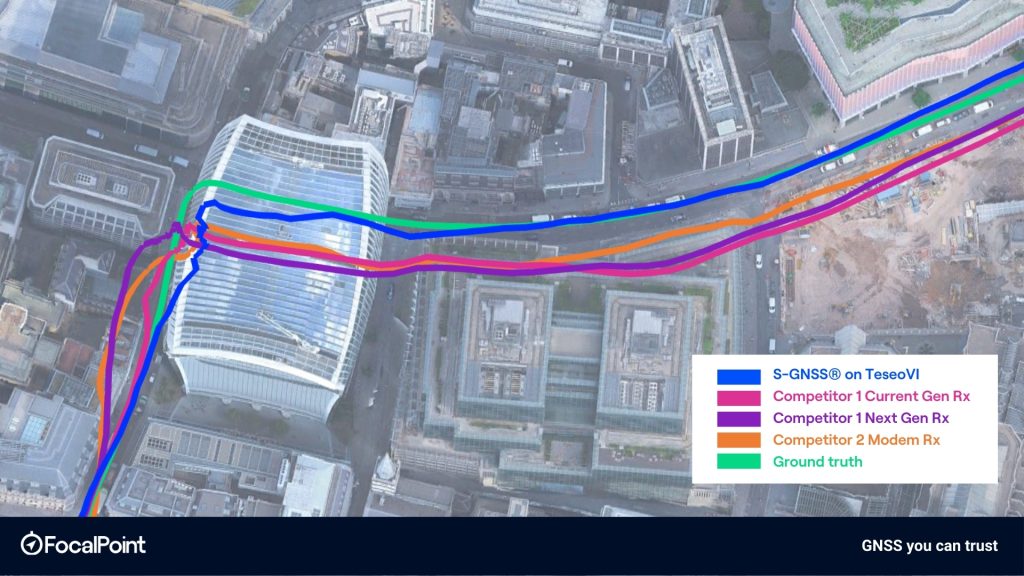
Figure 3: Highlight 1 – turning the corner around the ‘Walkie-Talkie’ building, Fenchurch Street
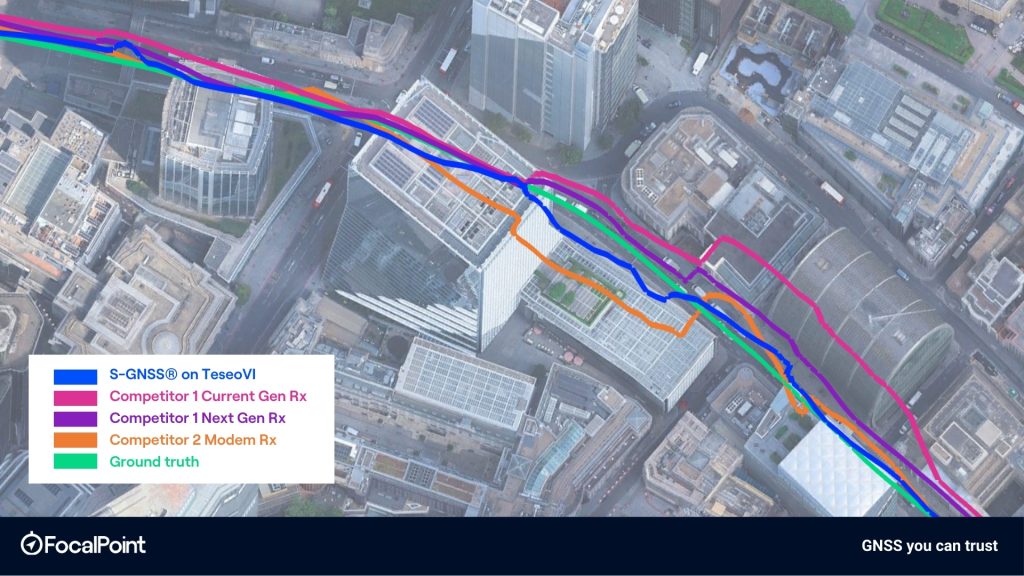
Figure 4: Highlight 2 – Camomile Street onto Wormwood Street
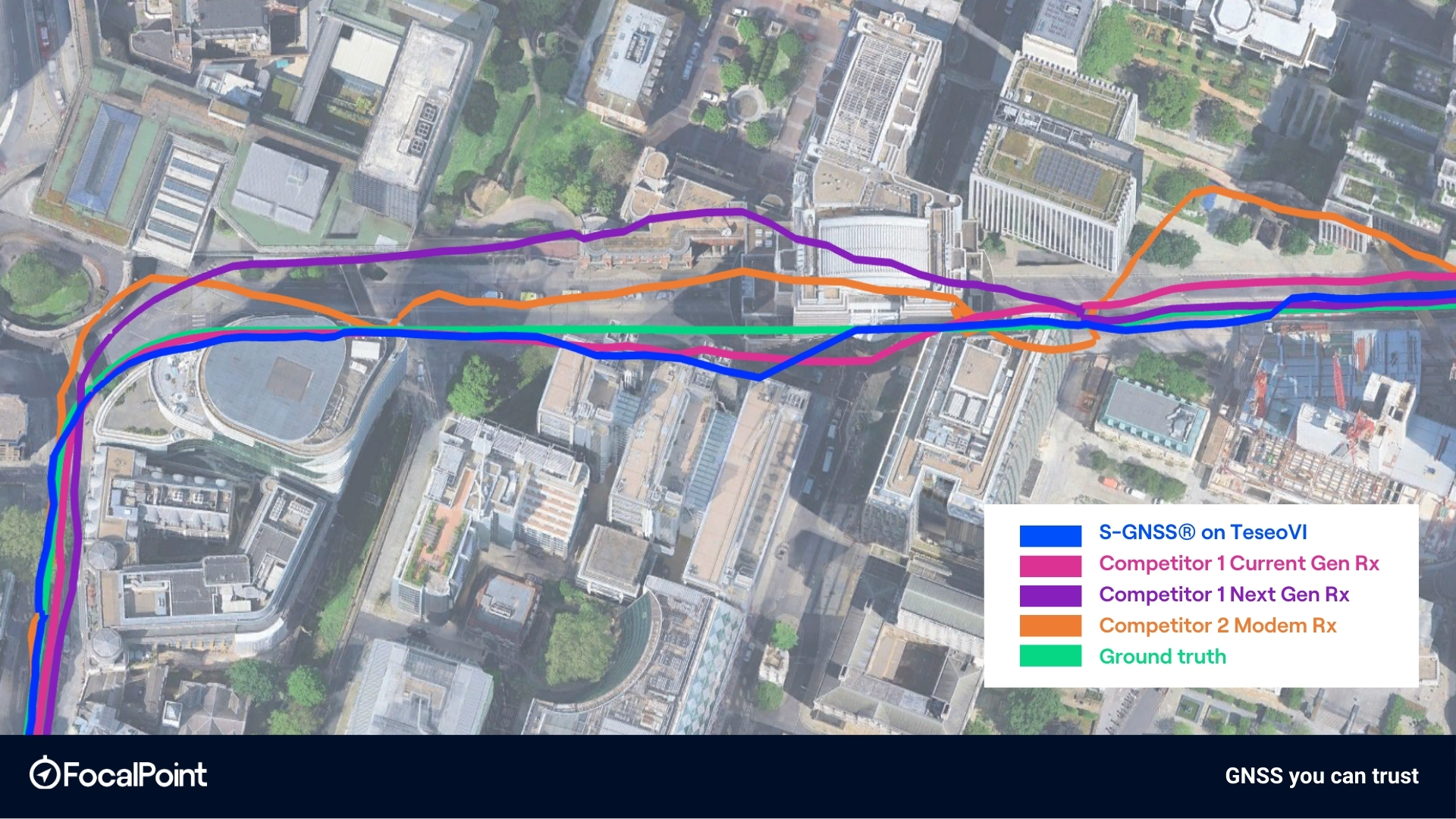
Figure 5: Highlight 3 – London Wall
Conclusion
The results demonstrate that the ST TeseoVI + S-GNSS solution delivers the strongest positioning performance across the evaluated urban route. At the 95% level (representative of tail performance in challenging conditions) TeseoVI + S-GNSS achieves 7.0 m, compared with 10.3–11.0 m for the standalone competitors and 21.2 m for the modem receiver, equating to a 32% reduction in the largest errors. This performance separation is visible across the full CDF curve, where the TeseoVI + S-GNSS solution consistently exhibits a leftward shift, indicating lower error at all probability levels.
The map-based trajectory comparisons further support these statistical results. In dense urban segments, including the corner around the the ‘Walkie-Talkie’ building, the Camomile Street to Wormwood Street transition, and along London Wall, the TeseoVI + S-GNSS trace shows tighter alignment to ground truth and reduced lateral dispersion relative to competitor receivers. Deviations observed in competitor solutions, particularly during turns and in street canyons, are visibly reduced in the S-GNSS-enabled solution.
Across both statistical and spatial analyses, the data shows that integrating S-GNSS with the ST Teseo platform provides measurable and consistent improvement in urban positioning performance, delivering the most accurate horizontal solution among the evaluated receivers.
For a detailed analysis and to see how S-GNSS can be integrated into your roadmap, contact us using the form below.